
Benzotriazole and its derivatives as metal deactivators
What is a metal deactivator?
Metal deactivators, also known as metal passivators, are agents used in both fuel oil and lubricating oil. They were first added to gasoline. Their main purpose is to passivate metals. In the process of fuel production and storage, they are additives that reduce the activity of metals due to concerns about the impact of metals on catalysts. Therefore, they are called passivators in the field of fuel oil. In the field of lubricating oil, their role is to reduce the activity of metals, especially copper. Copper can greatly increase the rate at which oil products are oxidized. Therefore, the activity of copper is reduced, so that it has less energy to catalyze the base oil, thereby improving the antioxidant capacity of the finished oil. It is precisely because of this role that many foreign scholars have defined this additive as an antioxidant. In China, they have also followed the trend and classified it into the number 5 (antioxidant + metal deactivator) category.
In principle, metal deactivators rely on the addition of additives to significantly reduce the activity of metals and indirectly improve the antioxidant capacity of oil products. In popular terms, this is a two-shot vaccine (inactivated type), which is very different from the principle of strong antioxidants such as phenols and amines. Therefore, it is more often called a metal deactivator in our field. It is precisely because of the different antioxidant methods that this agent can work together with real antioxidants, without interfering with each other and helping each other. Generally speaking, the dosage of this thing is very low, and a hundred ppm is enough to solve many problems.
What are the classifications of metal deactivators?
The following are the main classifications of metal deactivators and their detailed descriptions:
1. Benzotriazole derivatives (BTA)
Representative products:
CSAIL® T551(benzotriazole aldehyde-amine condensate)
Features: It has good antioxidant and anti-rust properties, can effectively inhibit the corrosion of corrosive substances in oil products on metal surfaces, and also has antioxidant functions. When CSAIL® T551 is used in combination with antioxidants, it has a significant synergistic effect.
2. Thiadiazole derivatives
Representative product:
CSAIL® T561 (2,5-dialkyl disulfide 1,3,4 thiadiazole)
Features: It has antioxidant and anti-corrosion properties and good anti-wear properties. It is widely used in internal combustion engine oils and can significantly improve the oxidation stability of gasoline engine oil. It can be used in anti-wear hydraulic oils to play a good role in resisting copper corrosion.
3. Di-salicylic acid propylene diamines
Representative product: N,N'-di-salicylic acid propylene diamine (my country's additive brand number is T1201)
Features: It is mainly used for fuel oil to improve its storage stability. It has been used in jet fuel since the 1980s to meet the increasingly stringent performance requirements of jet fuel.
4. Amines
Representative product: Zinc dialkyl dithiophosphate (ZDDP)
Features: It is one of the most commonly used metal deactivators, widely used in engine oils, and has good anti-wear and antioxidant properties.
There are not many types of metal deactivators in our field, only a few major categories, and compared with the oil refining industry, they are not core additives. Today we will talk about the first category.
Benzotriazole and its derivatives, benzotriazole is water-based, and derivatives are oil-based. Water-based ones are added to antifreeze and water-based products, and oil-based ones are added to oil. The molecular formula is as follows. The most typical product of this type of product is T551, which is our domestic name. There is actually no such brand abroad.
CSAIL® T551:N, N'-di-n-butylaminomethylenebenzotriazole
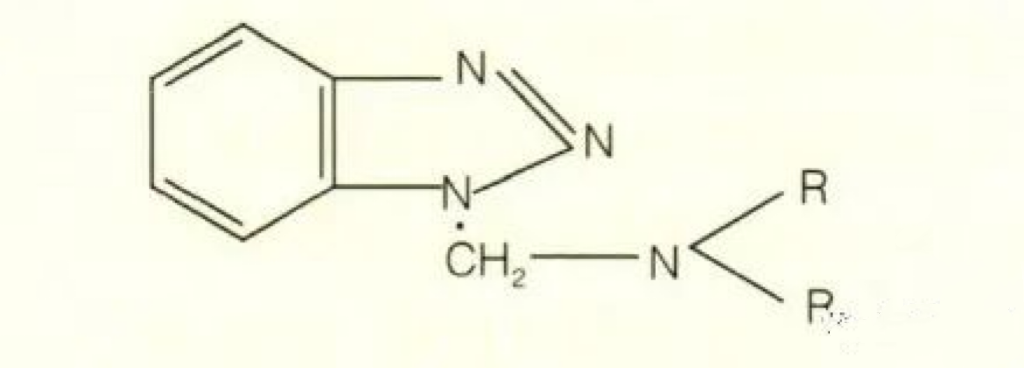
T551 was developed in China very early and is a fairly mature additive product, belonging to benzotriazole derivatives. The largest use of this product is industrial oil, such as turbine oil, hydraulic oil, bearing circulation oil, etc. It has a low dosage, fast effect, and good effect, and is warmly welcomed by everyone. However, this thing alone is not very meaningful for metal deactivation. It is generally used in combination with OSAIL® T501, a phenolic main antioxidant. OSAIL® T501 is a strong antioxidant, and CSAIL® T551 is a deactivated metal to help improve the antioxidant properties of oil products. This is the synergistic effect between additives, 1+1>2.
The new generation of benzotriazole deactivators, namely methyl benzotriazole and its derivatives, referred to as TTA, is CSAIL® 3900 of UNPChemicals. Like BTA, derivatives are oil-soluble and TTA is water-soluble.
The molecular formula is as follows:
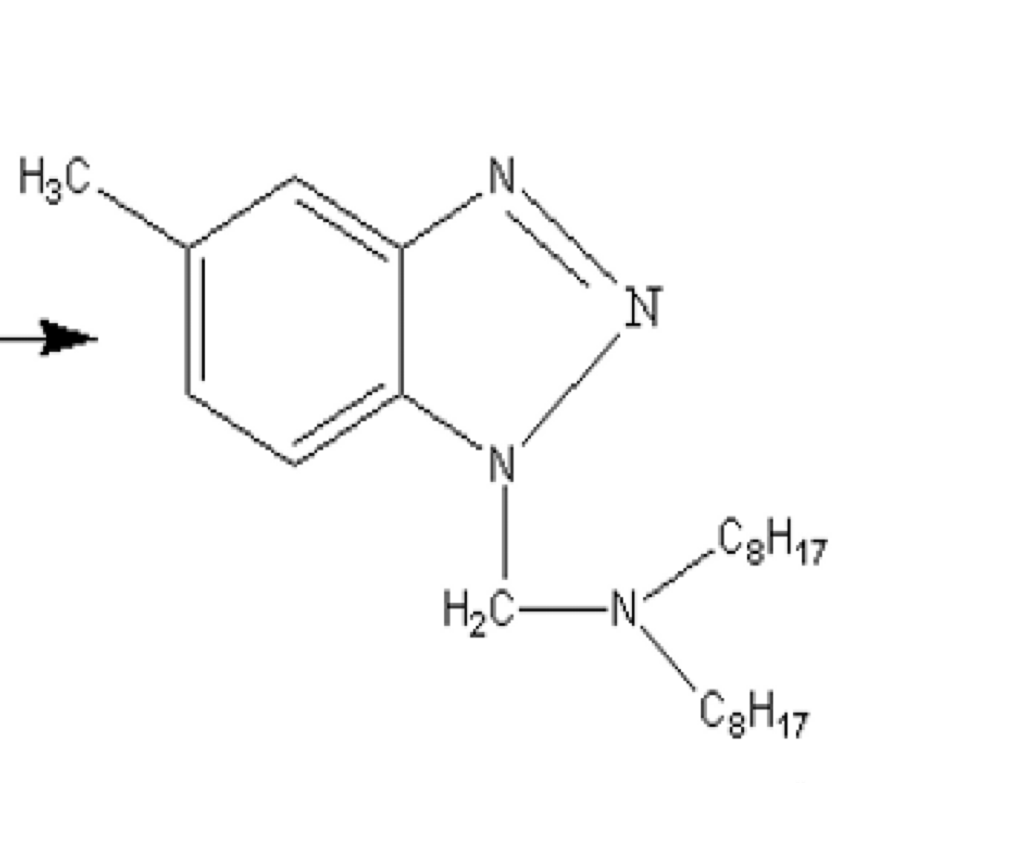
In fact, it has one more methyl group (on the benzene ring) than ordinary benzotriazole. Don't underestimate this extra methyl group. After introducing this methyl group, the following different product characteristics will appear:
First, TTA's corrosion inhibition on copper, that is, the deactivation will be better, and the dosage will be lower. This has been verified by many peers.
Secondly, after the introduction of methyl, the oil solubility of TTA derivatives is better. The most important thing is that TTA derivatives can significantly reduce TBN by selecting suitable amine groups, and are no longer afraid of ZDDP and MoDTC. In this way, TTA has more wings and can be used in engine oil. Engine oil antioxidants, phenols + amines + deactivators, a trinity, work in coordination. Therefore, some oil companies say that their oils are: multiple antioxidant technologies. I think this may be the reason, because there are only so many common antioxidant types.
Finally, TTA derivatives have better high temperature stability and stronger antioxidant ability. This background is also because the temperature of engine oil is generally higher than that of industrial oil, so TTA will be recognized by more customers. Now foreign products are generally methyl benzotriazole and its derivatives.
TTA can basically completely replace CSAIL® T551, and its application range is also wider. By matching with different amine structures, it is more conducive to the solubility of base oil, especially Class III oil and PAO (the purer the higher the solubility requirement), and with phenolic antioxidants, the metal activity is greatly reduced, which indirectly improves the antioxidant property of oil. Although copper corrosion is not a core indicator of engine oil, the bench VIII still exists, so it is still worth considering.
CSAIL® T551 was developed very early in China, and there are many suppliers. But in this era of TTA, there are fewer manufacturers instantly, but we can't always rely on them, we have to have an internal cycle. Today we will introduce a domestic TTA company, UNPChemicals, whose CSAIL® 3900 metal deactivator is a typical TTA derivative, and its performance is not bad. If you have time, you can try it yourself.
Oh, yes, there are some special characteristics. If the TTA dosage is not more than 0.1%, it can meet the food-grade certified additive formula, which is much better than BTZ.
Application of metal deactivators
In the oil refining industry, metal deactivators have two applications. One is to inhibit the catalytic effect of active metal ions (copper, iron, nickel, manganese, etc.) on the oxidation of oil products. It is often used in combination with antioxidants in light fuels such as gasoline, jet fuel, and diesel to improve the oxidation stability of oil products and extend the storage period. The second is to inhibit the influence of heavy metals (nickel, vanadium, copper, etc.) contained in the oil on the activity of the catalyst in the catalytic cracking of heavy oil. Antimony compounds are commonly used. But in the field of lubricating oil, there is basically no first-class function, only the second-class function. In addition, the dosage is very small, so the big names in this field are mainly fuel additives.